Inhibition of cathepsin B activity reduces degradation of DQ-collagen... | Download Scientific Diagram

Degradation of DQ-collagen IV was greater at an acidic pHe. Left (A, C,... | Download Scientific Diagram
Monitoring the Effects of MMP Inhibitors on Extracellular Matrix Degradation for use in Implant Protection

Biology | Free Full-Text | Monitoring Snake Venom-Induced Extracellular Matrix Degradation and Identifying Proteolytically Active Venom Toxins Using Fluorescently Labeled Substrates

Snail1 induced in breast cancer cells in 3D collagen I gel environment suppresses cortactin and impairs effective invadopodia formation - ScienceDirect

Acceleration of diabetic wound healing using a novel protease–anti-protease combination therapy | PNAS

Contribution of bone marrow macrophages to proteolysis of dQ-Collagen... | Download Scientific Diagram
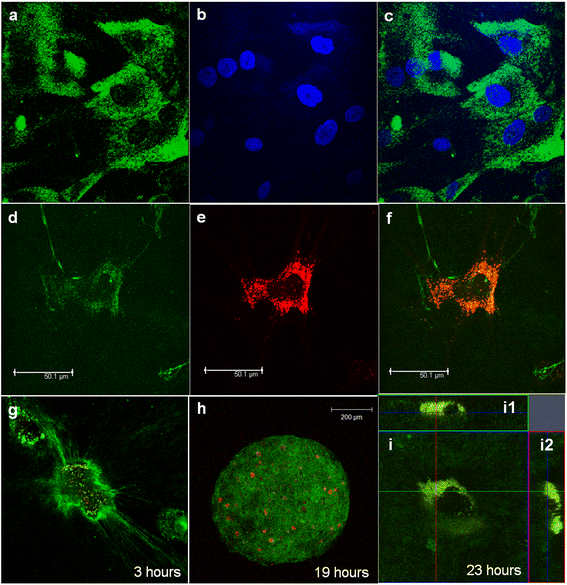
Protease inhibitors enhance extracellular collagen fibril deposition in human mesenchymal stem cells | Stem Cell Research & Therapy | Full Text

Proteolytic activity of TICs. (A) DQ-collagen IV TM proteolysis by TICs... | Download Scientific Diagram

Degradation of DQ-collagen IV was reduced by inhibition of cathepsin B.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Nitroxoline impairs DQ-collagen IV degradation in transformed and tumor... | Download Scientific Diagram

Uncaged inhibitor 1 reduces degradation of DQ-collagen IV by 3D MAME... | Download Scientific Diagram

Functional Imaging of Proteolysis: Stromal and Inflammatory Cells Increase Tumor Proteolysis - Mansoureh Sameni, Julie Dosescu, Kamiar Moin, Bonnie F. Sloane, 2003
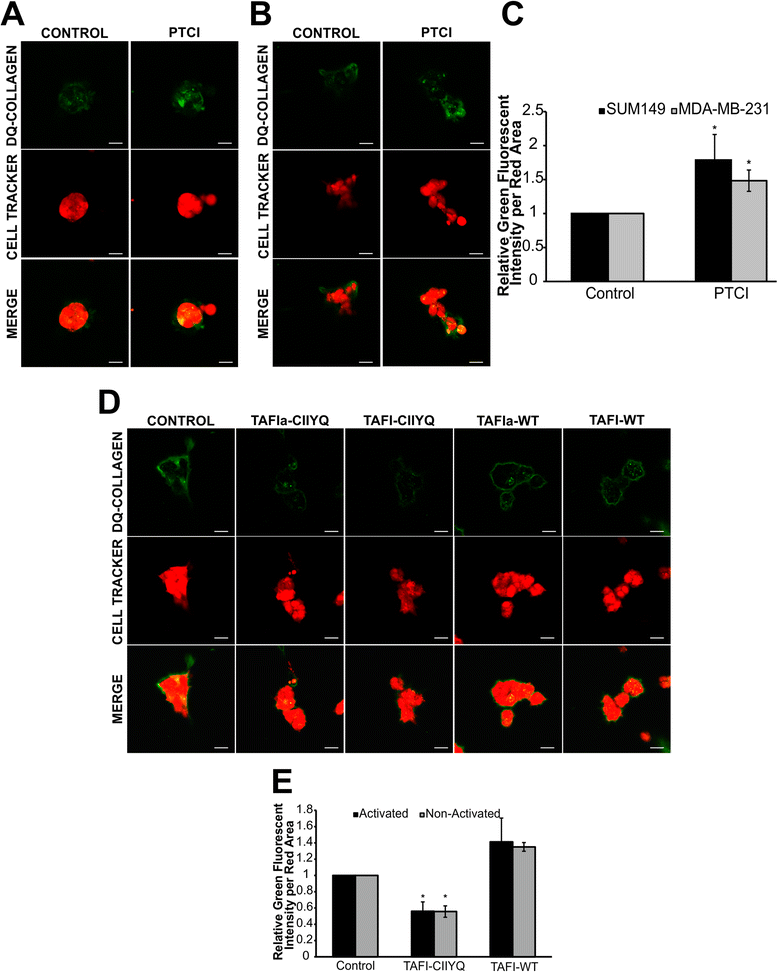
Activated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFIa) attenuates breast cancer cell metastatic behaviors through inhibition of plasminogen activation and extracellular proteolysis | BMC Cancer | Full Text

Fluorescent degradation products of DQ-collagen IV (A and B) colocalize... | Download Scientific Diagram

HGF increased degradation of DQ-collagen IV by MCF10.DCIS and SUM102 3D... | Download Scientific Diagram

New 3D-Culture Approaches to Study Interactions of Bone Marrow Adipocytes with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Cells. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Chemotherapy-induced collagen IV drives cancer cell invasion through activation of Src/FAK signaling | bioRxiv